Advanced Analytics
Introduction:
Businesses, organizations, and researchers in today’s data-driven world all want better understanding and more precise forecasts so they can make better decisions. The emergence of advanced analytics as the primary enabler is due to the breadth and depth of its many advanced approaches and procedures that convert data into useful knowledge. This blog will delve into the revolutionary power of advanced analytics, covering its many applications and methodologies.
Understanding Advanced Analytics:
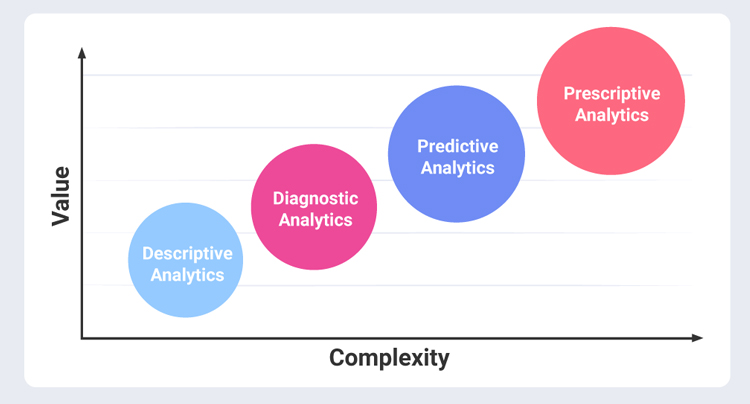
The term “advanced analytics” describes a wide range of methods for analyzing and making sense of large, complicated datasets. Advanced analytics dig deeper than simple descriptive statistics to uncover hidden trends, patterns, and linkages. It makes use of advanced methods of prediction and analysis, including machine learning, AI, and other algorithms.
Important Methods in Advanced Analytics:
- Machine learning (ML) is a branch of AI that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed to do so. Algorithms based on machine learning are able to learn from past data to produce more precise predictions in the future. From fraud detection and recommendation systems to picture recognition and NLP, this method has many potential uses.
- The term “predictive analytics” refers to the practice of leveraging past data and statistical algorithms to foretell potential future occurrences. It helps businesses foresee client actions, spot dangers, and enhance operational efficiency. Predictive analytics is used by businesses to better manage stock, set prices, and plan and execute marketing initiatives.
- The goal of data mining is to unearth useful information buried within large databases. Data mining techniques are useful for discovering hidden patterns and connections in massive datasets. It’s an integral part of industries like banking, medicine, and online shopping.
- Data mining from texts (Natural Language Processing): Text analytics, enabled by natural language processing (NLP), allows for the processing and analysis of textual data. This method can help businesses gain useful insights into how to improve customer experiences and make data-driven decisions by extracting sentiments, subjects, and key phrases from customer reviews, social media comments, and other textual sources.
The Obstacles and Opportunities of Advanced Analytics:
Although advanced analytics presents numerous advantages, it also creates certain difficulties.
- Integrity and completeness of data are crucial to the success of advanced analytics projects. In order to gain trustworthy insights, it is essential to guarantee correct data collection, purification, and integration.
- The use of sophisticated analytics calls on the talents and knowledge of data scientists, analysts, and domain specialists. Organizations’ efforts to maximize this resource may be hampered by a lack of available talent.
- The sensitive nature of the data commonly handled by advanced analytics raises questions of ethics and privacy. It is critical for businesses to protect customer information and follow all applicable laws and regulations.
Conclusion:
For enterprises and organizations of all stripes, advanced analytics has become a game-changer by facilitating data-driven decision making. These cutting-edge methods, which include predictive analytics, machine learning, and natural language processing, present unheard-of chances to gain actionable insights and enhance operational efficiency. The future of data-driven success depends on firms continuing to invest in talent, data quality, and ethical considerations as they realize the potential of advanced analytics. Businesses can improve their future prospects by embracing sophisticated analytics in order to acquire a competitive edge, respond to changing market conditions, and encourage creative problem solving.
